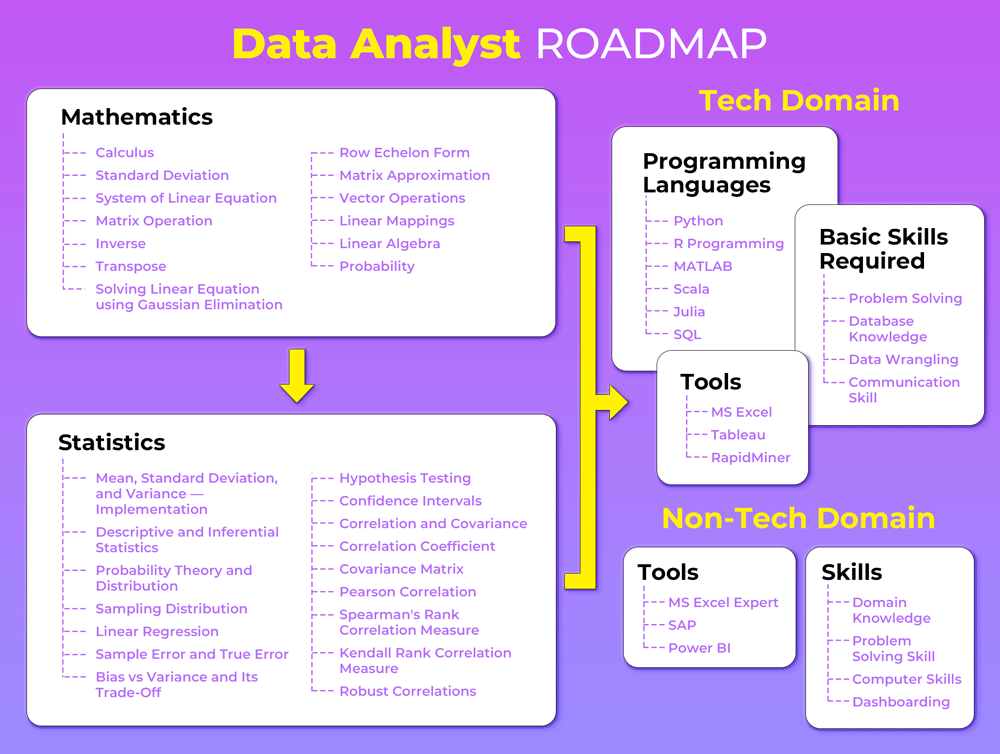

If you want to become a Data Analyst, having a clear roadmap is essential. Data analytics is one of the most in-demand careers today, combining mathematics, statistics, programming, tools, and business skills.
This SEO-friendly guide explains the complete Data Analyst Roadmap, from fundamentals to advanced skills, helping beginners and students plan their learning path efficiently.
What Is a Data Analyst?
A Data Analyst collects, cleans, analyzes, and visualizes data to help organizations make better decisions. They work with numbers, tools, and business problems to find meaningful insights from raw data.
1. Mathematics for Data Analysts
Mathematics builds the foundation of data analysis. You don’t need advanced math like a PhD, but core concepts are essential.
Key Topics to Learn:
- Calculus (basics)
- Standard Deviation
- System of Linear Equations
- Matrix Operations (Inverse, Transpose)
- Solving Linear Equations using Gaussian Elimination
- Vector Operations
- Linear Algebra
- Probability
- Linear Mappings
- Matrix Approximation
- Row Echelon Form
Why it matters:
Math helps you understand how algorithms work and how data behaves under different transformations.
2. Statistics for Data Analysis
Statistics is the heart of data analytics. Most real-world decisions are based on statistical insights.
Important Statistical Concepts:
- Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Probability Theory and Distributions
- Sampling Distribution
- Linear Regression
- Hypothesis Testing
- Confidence Intervals
- Correlation and Covariance
- Pearson Correlation
- Spearman and Kendall Rank Correlation
- Bias vs Variance Trade-off
- Robust Correlations
Why it matters:
Statistics allows you to validate assumptions, test hypotheses, and measure relationships between variables.
3. Programming Languages for Data Analysts (Tech Domain)
Programming helps you analyze large datasets and automate tasks.
Must-Learn Languages:
- Python (most important)
- R Programming
- SQL
- MATLAB
- Scala
- Julia
Pro Tip:
Start with Python + SQL — they cover 80% of real-world data analyst tasks.
4. Data Analyst Tools (Tech Domain)
Tools help you analyze and visualize data quickly.
Essential Tools:
- MS Excel
- Tableau
- RapidMiner
Why tools matter:
Companies expect analysts to work efficiently using industry-standard tools.
5. Basic Skills Required for Data Analysts
Technical skills alone are not enough. You also need soft and analytical skills.
Core Skills:
- Problem Solving
- Database Knowledge
- Data Wrangling
- Communication Skills
Tip:
A good data analyst can explain complex data insights in simple language.
6. Non-Technical Domain Tools
Business and enterprise tools add value to your analytics profile.
Important Non-Tech Tools:
- MS Excel (Advanced / Expert level)
- SAP
- Power BI
Why learn them:
Many companies rely heavily on dashboards and enterprise reporting systems.
7. Non-Technical Skills for Data Analysts
These skills help you stand out in interviews and real projects.
Key Non-Tech Skills:
- Domain Knowledge (Finance, Healthcare, Marketing, etc.)
- Problem-Solving Ability
- Computer Skills
- Dashboard Designing
How to Follow This Data Analyst Roadmap?
Step-by-Step Learning Order:
- Start with Mathematics basics
- Learn Statistics deeply
- Move to Python and SQL
- Practice using Excel, Tableau, Power BI
- Build real-world projects
- Improve communication and business understanding
Career Opportunities After Learning Data Analytics
- Data Analyst
- Business Analyst
- Reporting Analyst
- Operations Analyst
- Junior Data Scientist