Introduction: Why Learn DSA in Python?
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) form the core foundation of programming and problem-solving. If you want to crack coding interviews, write efficient programs, or become a strong software engineer, DSA is non-negotiable.
Python is one of the best languages to learn DSA because of its simple syntax, readability, and powerful built-in features. In this blog, we will cover all major DSA concepts in Python, explained in simple words with practical understanding.
1. Arrays in Python
Arrays store elements in contiguous memory locations and are accessed using indexes.
In Python, lists are commonly used to represent arrays.
Key concepts:
- Index-based access
- Fast read operations
- Fixed logical structure
Arrays are widely used in searching, sorting, and algorithm problems.
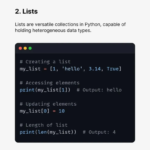
2. Lists in Python
Lists are dynamic and flexible data structures in Python.
Why lists are important:
- Can store multiple data types
- Support insertion, deletion, and updates
- Used as base for stacks and queues
Lists are one of the most frequently used data structures in Python-based DSA.
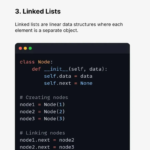
3. Linked Lists
Linked Lists store data in nodes, where each node points to the next one.
Types of Linked Lists:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Why use Linked Lists?
- Dynamic memory usage
- Efficient insertion and deletion
Linked lists are heavily asked in interviews and problem-solving rounds.
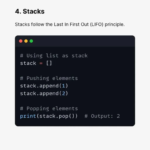
4. Stacks (LIFO)
Stacks follow the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle.
Common operations:
- Push
- Pop
- Peek
Real-world uses:
- Undo/Redo operations
- Function calls
- Expression evaluation
In Python, stacks are commonly implemented using lists.
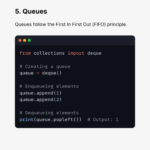
5. Queues (FIFO)
Queues follow the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle.
Applications of queues:
- Task scheduling
- CPU job processing
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Python provides efficient queue handling using collections.deque.
6. Hash Tables (Dictionaries)
Hash tables store data in key-value pairs and provide very fast lookup.
In Python, dictionaries act as hash tables.
Why hash tables are powerful:
- O(1) average lookup time
- Used in caching
- Frequency counting
- Fast searching problems
7. Trees
Trees represent hierarchical data structures.
Common tree types:
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree (BST)
- Heap
Use cases:
- File systems
- Databases
- Decision trees
Tree-based problems are very common in DSA interviews.
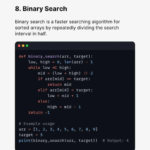
8. Binary Search
Binary Search is an efficient searching algorithm that works on sorted data.
Time Complexity:
O(log n)
Why it matters:
- Extremely fast
- Used in competitive programming
- Base for many advanced algorithms
Understanding binary search deeply is essential for DSA mastery.
9. Graphs
Graphs consist of vertices (nodes) and edges (connections).
Graph representations:
- Adjacency List
- Adjacency Matrix
Applications:
- Social networks
- Google Maps
- Recommendation systems
Graph algorithms like BFS, DFS, and shortest path are advanced but powerful DSA topics.
Why DSA in Python Is Important for Careers
- Helps crack technical interviews
- Improves logical thinking
- Required for product-based companies
- Essential for software engineering, backend, and AI roles