
Data Engineering has quietly become one of the most powerful and highest-paying careers in the tech ecosystem. While everyone talks about Data Science and AI, it is Data Engineers who build the backbone that makes all analytics, dashboards, and machine learning possible.
If you are:
- From a non-IT background (mechanical, civil, electrical, commerce, science)
- Confused between Data Analytics vs Data Engineering
- Looking for a clear, job-oriented roadmap
- Planning to enter tech without getting lost in random tools
What Is Data Engineering (In Simple Words)?
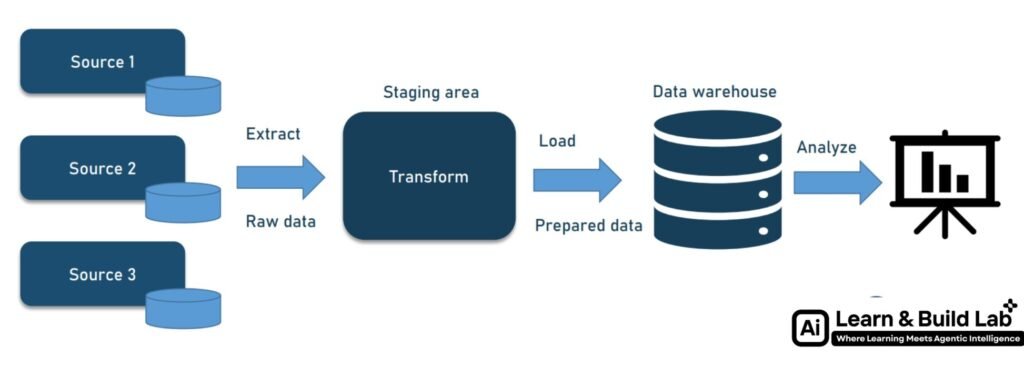
Data Engineering is about designing, building, and maintaining systems that:
- Collect data from multiple sources
- Clean and process that data
- Store it efficiently
- Make it available for analytics, dashboards, and AI models
A Data Engineer ensures that data is:
- Reliable
- Scalable
- Fast
- Secure
Without Data Engineers:
- Data Analysts can’t analyze
- Data Scientists can’t build models
- Businesses can’t take decisions
Why Data Engineering Is a Strong Career Choice in 2025
Here’s why Data Engineering stands out:
1. High Demand, Low Supply
Companies struggle to find good Data Engineers because the role requires:
- Programming
- Databases
- Big data tools
- Cloud knowledge
- System thinking
Most people learn only one part — Data Engineers connect everything.
2. Better Stability Than Trend-Based Roles
Tools may change, but core data engineering concepts remain the same:
- SQL
- Data modeling
- Pipelines
- Distributed systems
This makes the career future-proof.
3. Excellent Salary Growth
In India:
- Entry-level Data Engineer: ₹6–10 LPA
- Mid-level: ₹12–20 LPA
- Senior: ₹25 LPA+
Remote & global roles pay even more.
Data Analytics vs Data Engineering: Which Should You Choose?
This is the most common confusion, especially for non-IT students.
Data Analytics
- Focus: Insights, reports, dashboards
- Tools: Excel, SQL, Power BI, Tableau
- Entry barrier: Low
- Coding: Minimal
Data Engineering
- Focus: Data pipelines, systems, infrastructure
- Tools: Python, SQL, Spark, Kafka, Cloud
- Entry barrier: Medium
- Coding: Strong
The Smart Path for Non-IT Students
Start with Data Analytics → Move to Data Engineering
Why?
- Analytics builds confidence with data
- SQL becomes strong
- You understand business context
- Transition becomes smooth instead of overwhelming
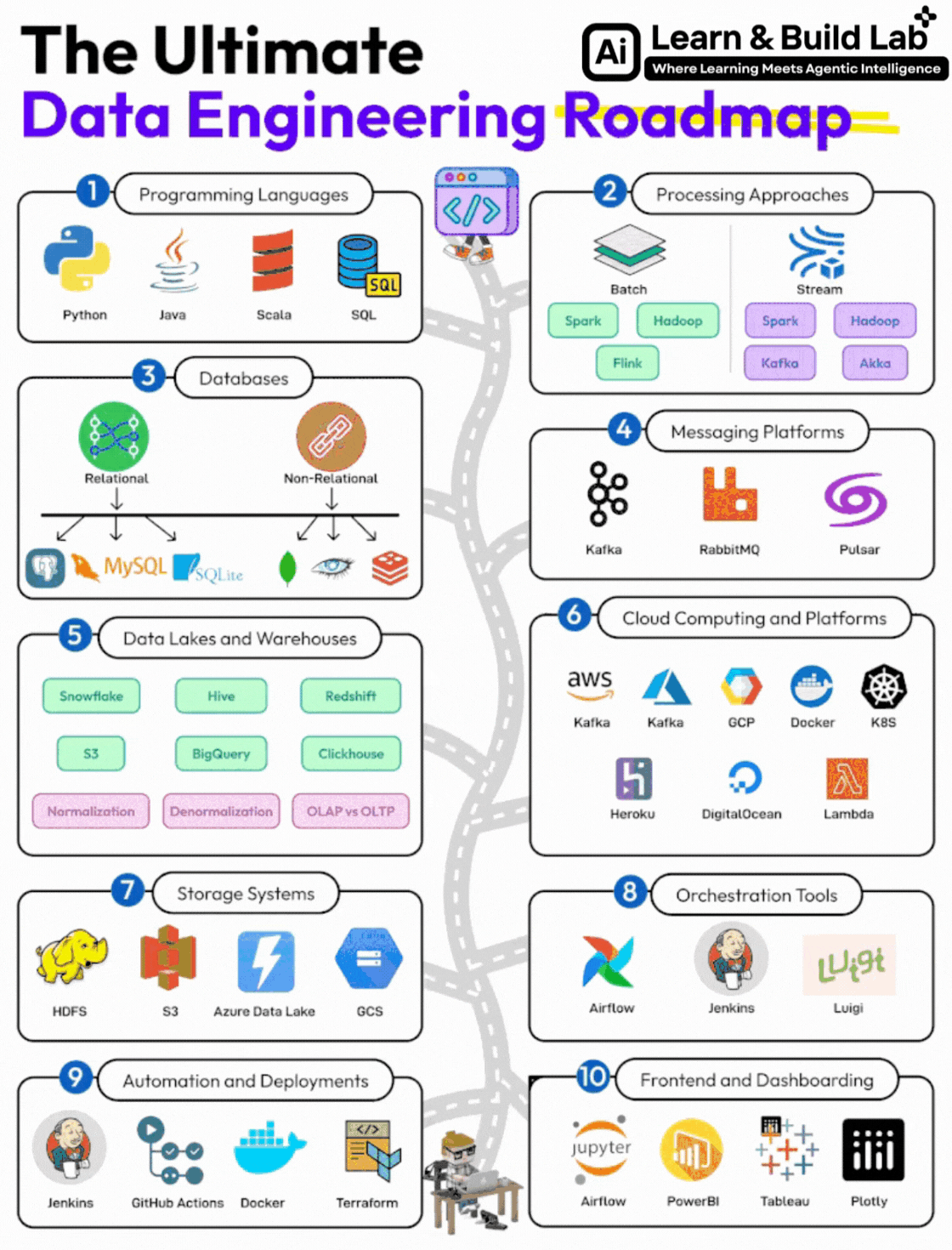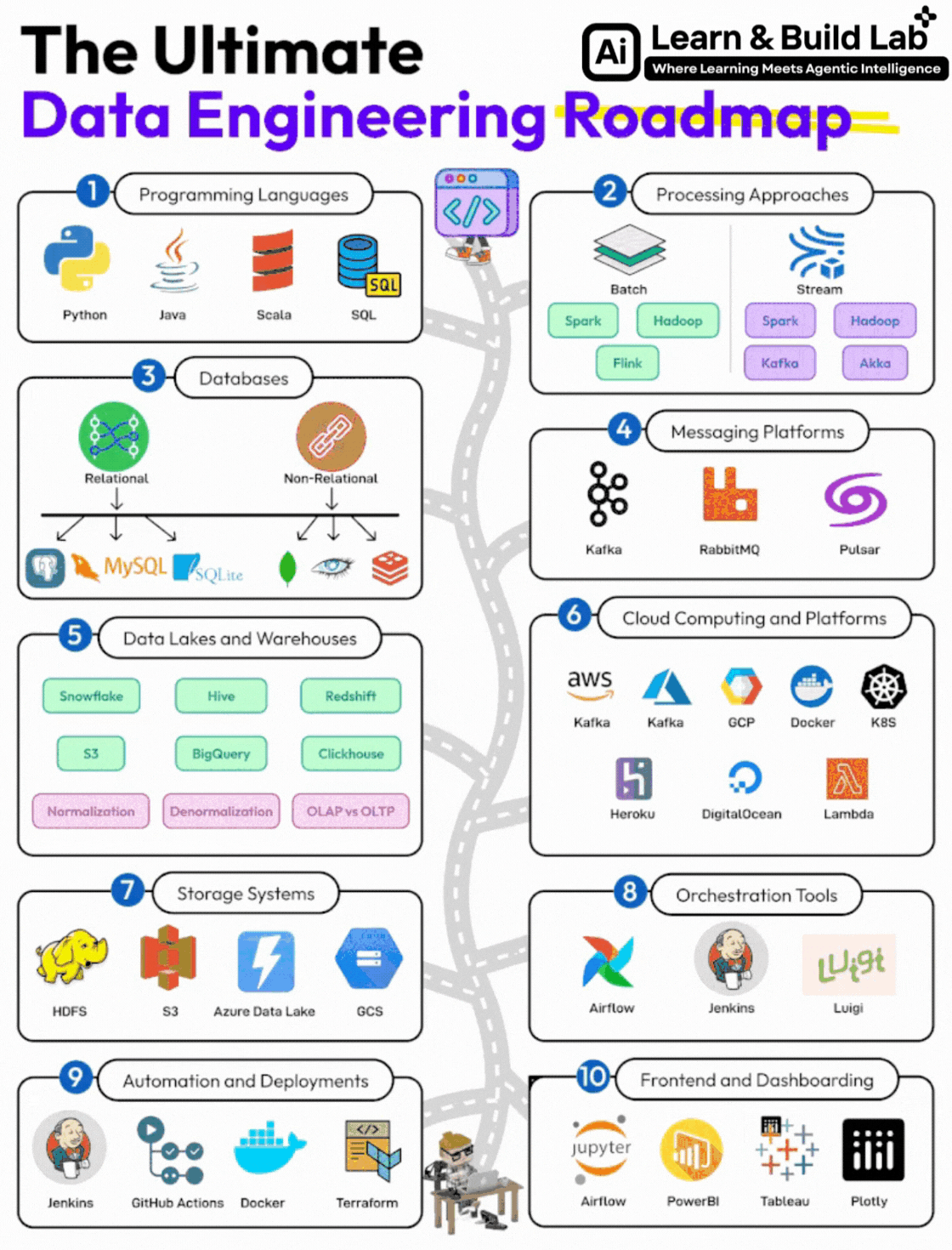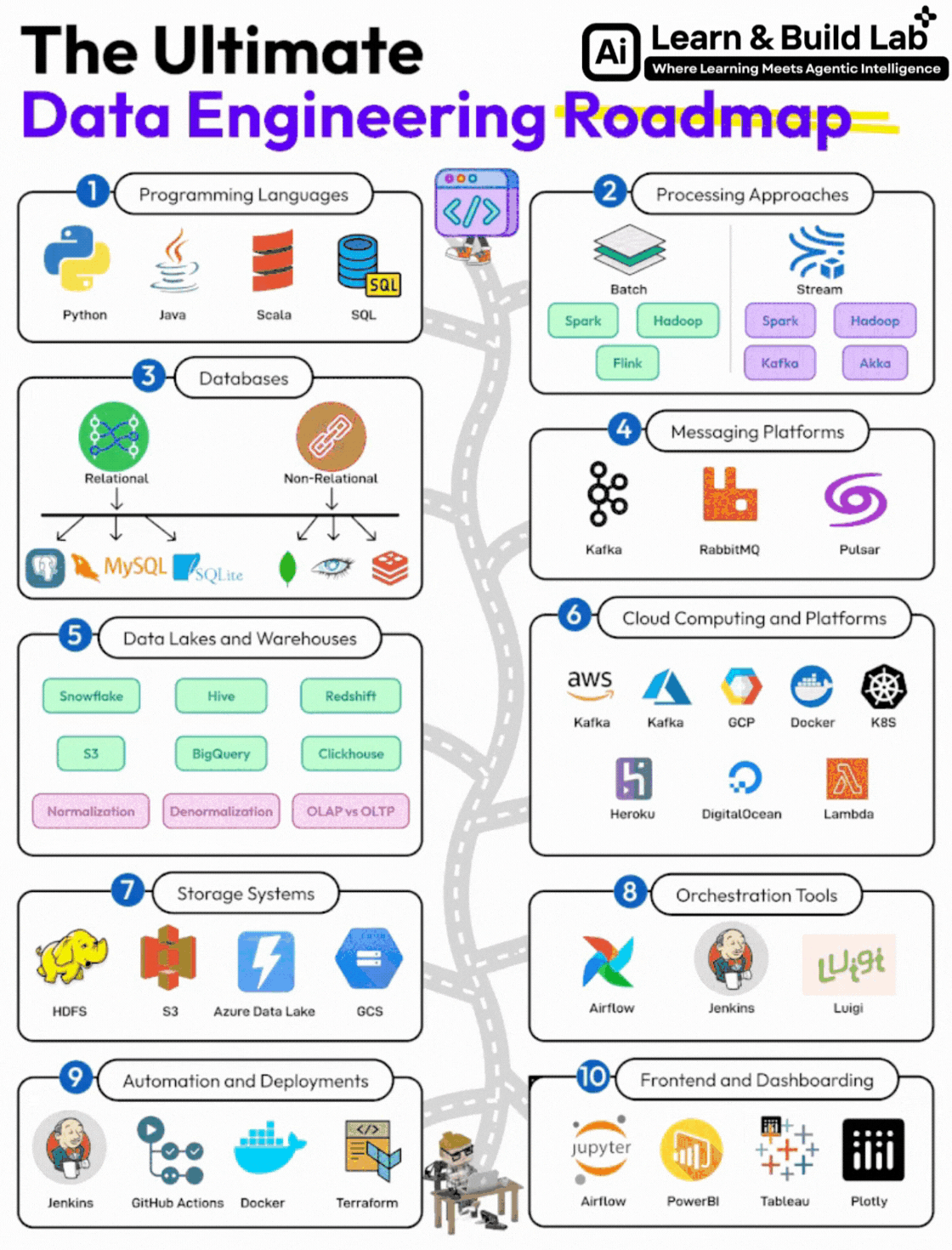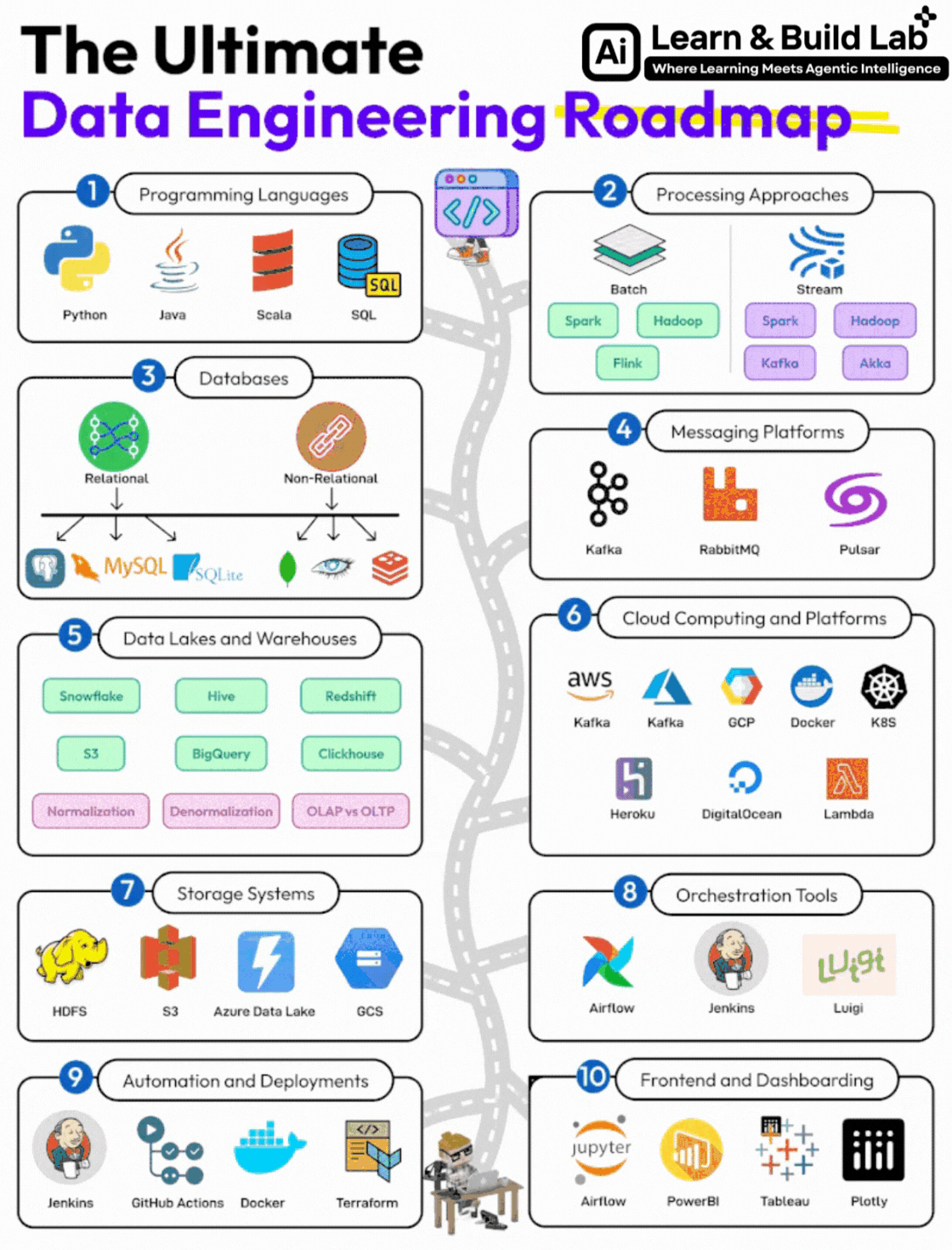
The Complete Data Engineering Roadmap (Step-by-Step)
Let’s now break down the full roadmap shown in the image — with clarity on:
- What to learn
- Why it matters
- How deep you need to go
Step 1: Programming Languages (Foundation Layer)
1. Python (Mandatory)
Python is used for:
- Data ingestion
- ETL pipelines
- Automation
- APIs
What you should learn:
- Variables, loops, functions
- Lists, dictionaries, sets
- File handling
- Pandas basics
- Writing clean, modular code
You don’t need advanced Python at the start — clarity > complexity.
2. SQL (Non-Negotiable Skill)
SQL is the most important skill for a Data Engineer.
You must master:
- SELECT, WHERE, GROUP BY
- JOINs (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT)
- Subqueries
- Indexing basics
- Query optimization
- Window functions (ROW_NUMBER, RANK)
Many candidates fail interviews only because of weak SQL.
3. Java / Scala (Bonus but Powerful)
Used heavily in:
- Apache Spark
- Big data frameworks
You don’t need to be a hardcore Java developer, but you should:
- Understand syntax
- Read code
- Write basic programs
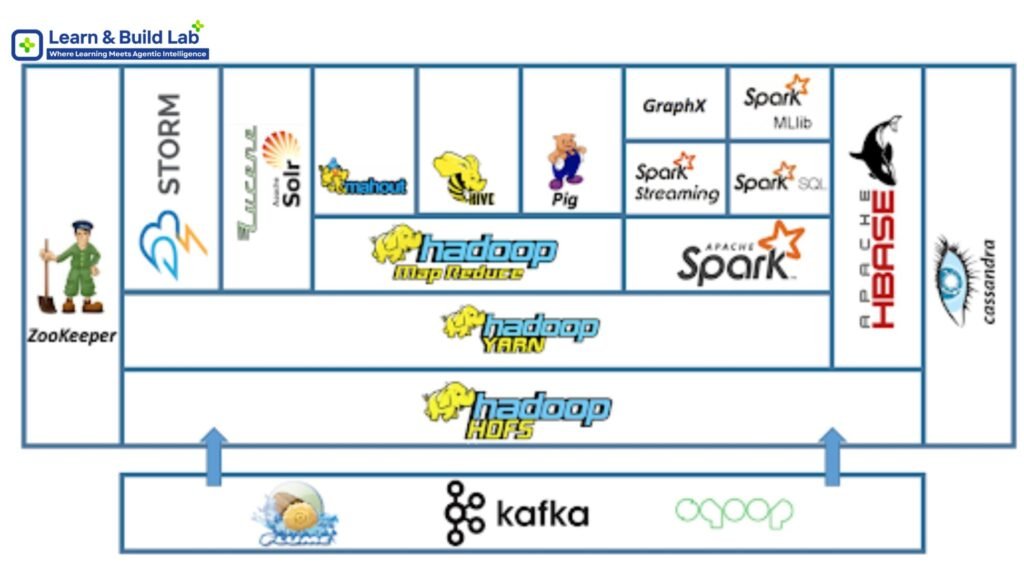
Step 2: Data Processing Approaches
Data is processed in two main ways:
1. Batch Processing
Data is processed in chunks (hourly, daily).
Tools:
- Apache Spark
- Hadoop
- Flink
Used in:
- Reports
- Historical analysis
- ETL jobs
2. Stream Processing
Data is processed in real-time.
Tools:
- Kafka
- Spark Streaming
- Akka
Used in:
- Fintech transactions
- Real-time alerts
- Live dashboards
Companies love engineers who understand both.
Step 3: Databases (Core Knowledge)
Relational Databases (RDBMS)
Examples:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- SQLite
You must understand:
- Tables & relationships
- Primary & foreign keys
- Normalization
- Transactions
NoSQL Databases
Examples:
- MongoDB
- Cassandra
- Redis
Used when:
- Data is unstructured
- High scalability is needed
- Low latency is required
Interviewers often ask:
“Why NoSQL over SQL?”
Step 4: Messaging & Event Streaming Platforms
These tools allow systems to talk to each other asynchronously.
Key Tools:
- Apache Kafka
- RabbitMQ
- Apache Pulsar
Kafka is especially important.
You should understand:
- Producers & consumers
- Topics & partitions
- Message durability
- Exactly-once vs at-least-once delivery
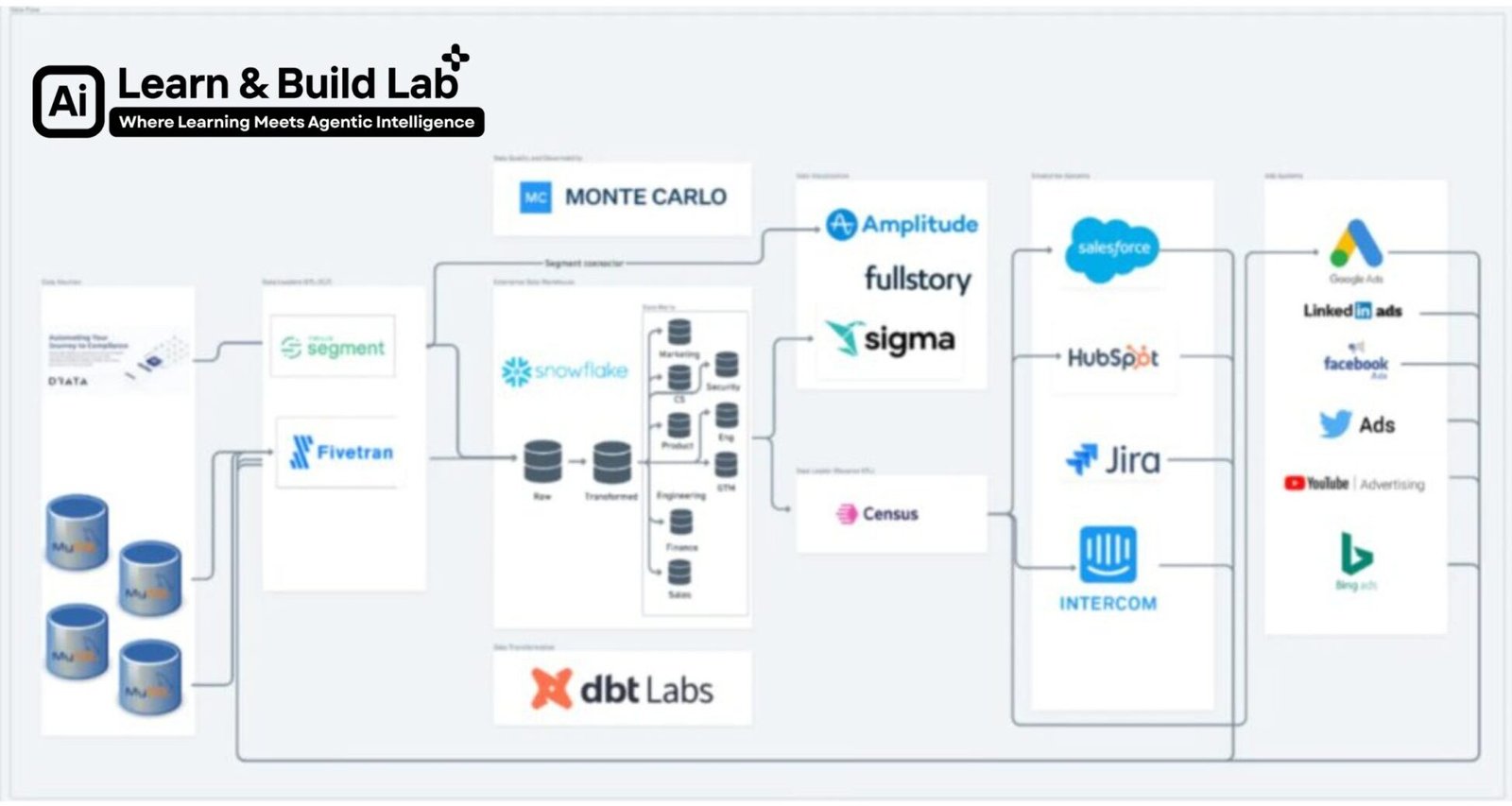
Step 5: Data Lakes & Data Warehouses
This is where engineering meets analytics.
Data Lakes
Store raw data.
Examples:
- AWS S3
- Azure Data Lake
Data Warehouses
Store processed, structured data.
Examples:
- Snowflake
- Redshift
- BigQuery
- ClickHouse
Concepts to master:
- OLTP vs OLAP
- Star vs Snowflake schema
- Denormalization
- Cost optimization
Step 6: Cloud Computing (Career Multiplier)
Modern Data Engineers must know cloud.
Major Platforms:
- AWS
- Azure
- Google Cloud
Key services:
- Storage (S3, GCS)
- Compute
- Managed databases
- Serverless (Lambda)
Also learn:
- Docker (containers)
- Kubernetes (basic understanding)
Cloud knowledge alone can increase your salary by 30–40%.
Step 7: Storage Systems
Understand how large-scale data is stored.
Tools:
- HDFS
- AWS S3
- Azure Data Lake
- Google Cloud Storage
Focus on:
- Distributed storage
- Fault tolerance
- Cost vs performance trade-offs
Step 8: Orchestration Tools
Used to schedule and monitor pipelines.
Popular tools:
- Apache Airflow
- Jenkins
- Luigi
You should know:
- DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs)
- Job dependencies
- Error handling
- Retries & alerts
Step 9: Automation & Deployment
This separates students from professionals.
Learn:
- Git & GitHub
- CI/CD pipelines
- Docker images
- Terraform basics (Infrastructure as Code)
Companies want engineers who can deploy, not just code.
Step 10: Frontend & Dashboarding (Supporting Skill)
Data Engineers don’t build dashboards daily, but must understand them.
Tools:
- Power BI
- Tableau
- Plotly
- Jupyter Notebook
This helps in:
- Collaboration with analysts
- Understanding data consumption
- Designing better pipelines
Projects: The Real Secret to Getting Hired
Certificates don’t get you hired. Projects do.
Must-have projects:
- Batch ETL pipeline using Python + SQL
- Real-time pipeline using Kafka
- Data warehouse model
- Cloud-based data pipeline
- End-to-end project (source → dashboard)
Even 3–4 strong projects can beat a long resume.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Learning tools without understanding concepts
- Skipping SQL
- Ignoring system design
- Only watching videos, not building
- Running behind trends blindly
Final Career Advice for Non-IT Students
If you are serious:
- Start small
- Be consistent
- Build projects
- Focus on fundamentals
- Learn how systems work, not just syntax
Data Engineering is not a shortcut career, but it is a strong, long-term career.
Conclusion
Data Engineering is the backbone of the modern data world. With the right roadmap, discipline, and hands-on learning, any motivated learner — even from a non-IT background — can break into this field.